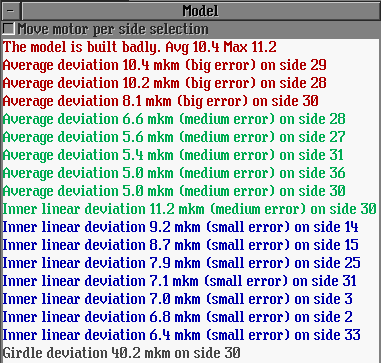
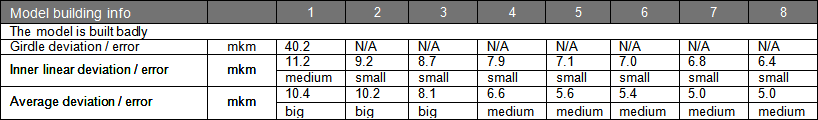
|
Helium Polish 5.4 is available for download at September 6, 2011.
More precise definition of diamond density |
|
The new version Helium Polish 5.4 uses a more precise value of the Diamond Density, 3,51524 g/cm3. It leads to more precise calculation of the weights of polished diamonds. The Density value of 3,522 g/cm3 was used in the previous versions of the software.
New measurements of Heights for Pavilion and Girdle |
|
The new version of Helium Polish measures Pavilion and Girdle heights in models in a new way.
A detailed description of the old measurements of the Crown height, Pavilion depth, and Girdle height parameters can be found here.
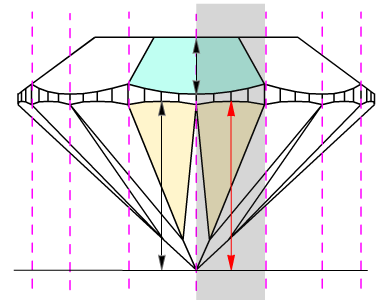
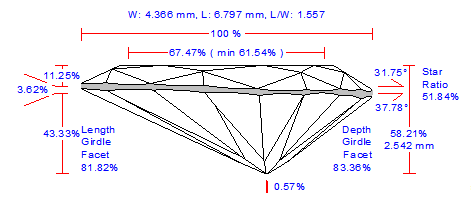
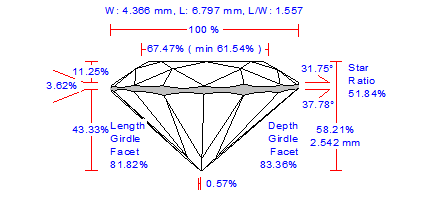
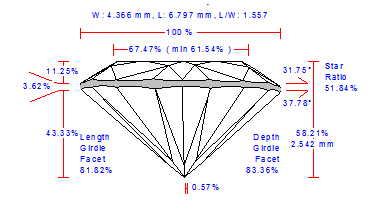
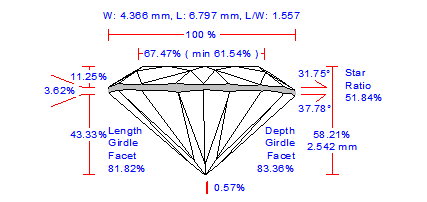
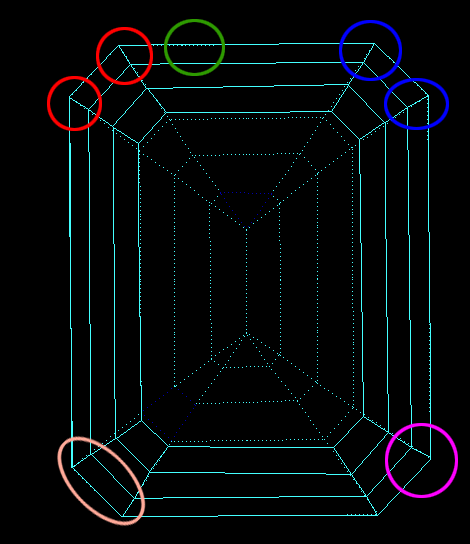
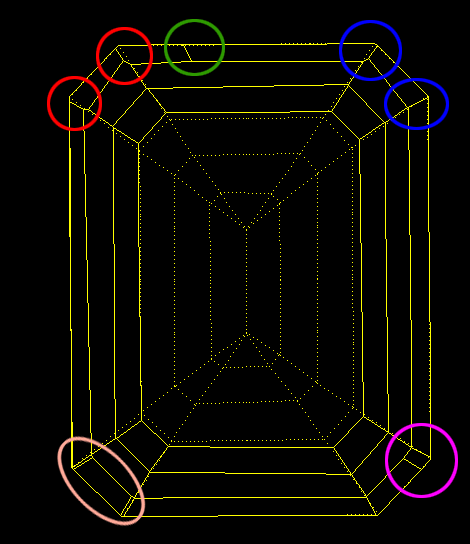
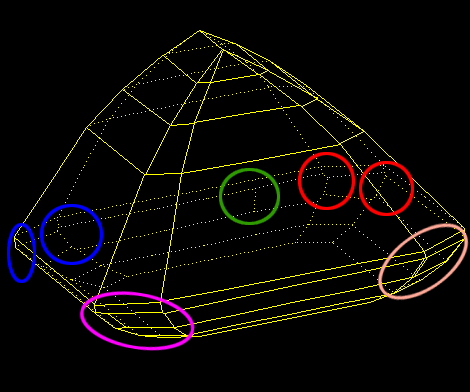
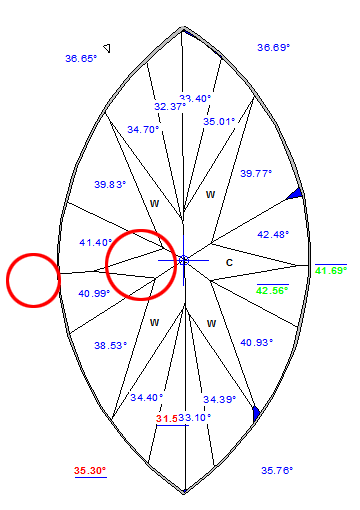
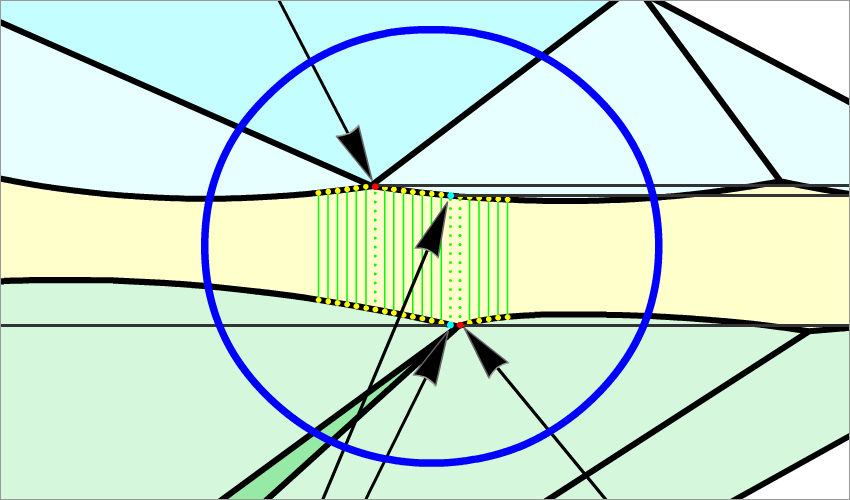
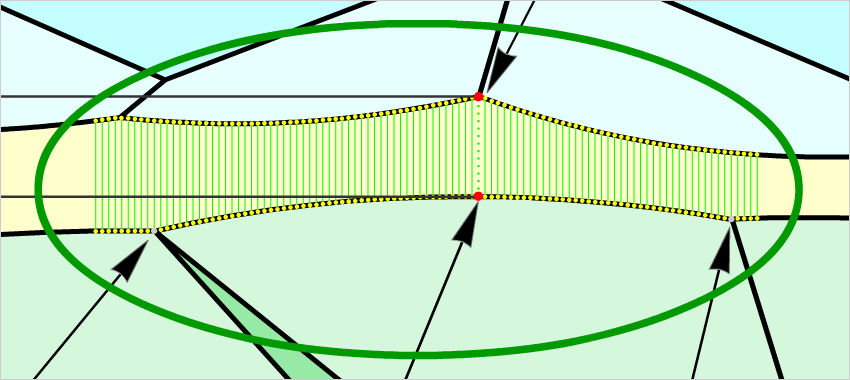
For cuttings with a big azimuthal difference between the Crown bezel point and the corresponding Pavilion bezel point, the sum of Crown height, Pavilion depth, and Girdle height is not equal to Total height. This always happens when the quantity of main crown facets is not equal to the quantity of main pavilion facets (Figure 1).
Figure 1
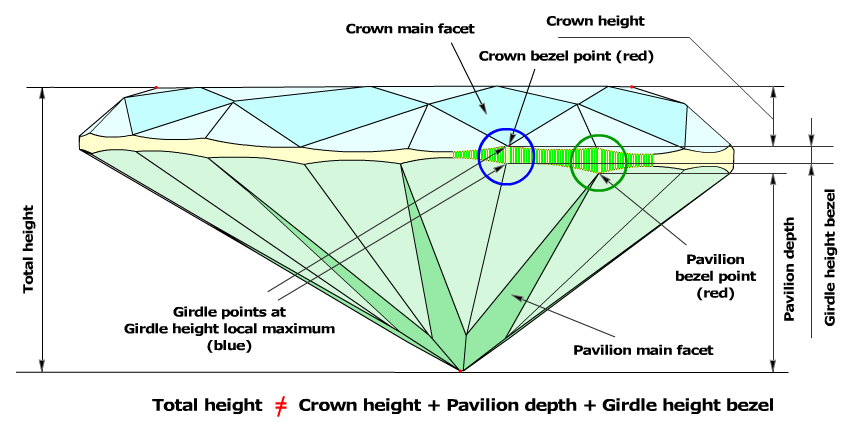
Figure 1, enlarged view
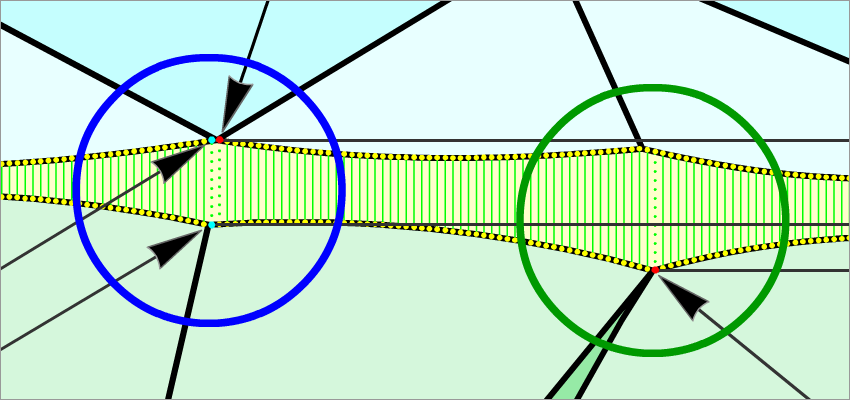
To get rid of this disparity, we have introduced a new method, according to which the Crown bezel points determine the measurement zones of the following parameters: Crown height, Pavilion height, and Girdle height bezel.
New method of estimating Crown height, Pavilion height and Girdle height
- The software finds the Crown bezel point on the upper girdle curve, by the same method as in the previous versions.
- Then it finds the closest (by azimuth) Pavilion bezel point or the Pavilion bone point on the lower girdle curve, by the same method as in the previous versions. if there are no Pavilion bezel point or Pavilion bone point around Crown bezel point, it could be just a point on a lower girdle curve, with the same azimuth as Crown bezel point. Let us call it the Pavilion height point.
- The distance, along diamond's axis that perpendicular to table, between maximal distant culet point and this Pavilion height point is called Pavilion height in the new version of the software (Figure2a, 2b).
- The difference between azimuths of Crown bezel point and Pavilion height point is determined.
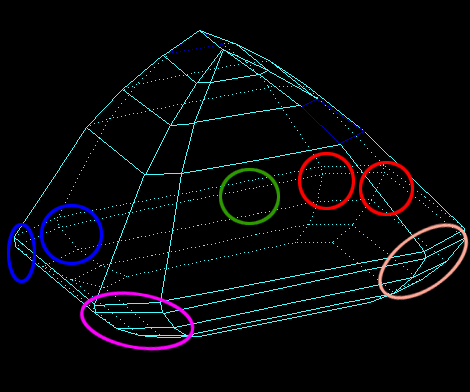
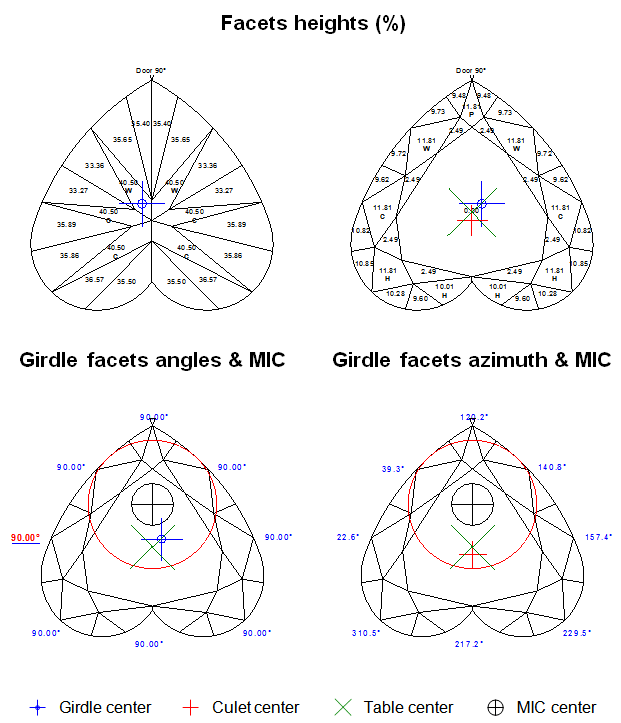
- If the difference between the azimuths of the Crown bezel point and the Pavilion Height point is less then 4 degrees, the value of the Girdle height bezel parameter is measured as the height between the the Crown bezel point and the opposite Pavilion height point (Figure 2a and Figure 2a, enlarged view).
Figure 2a
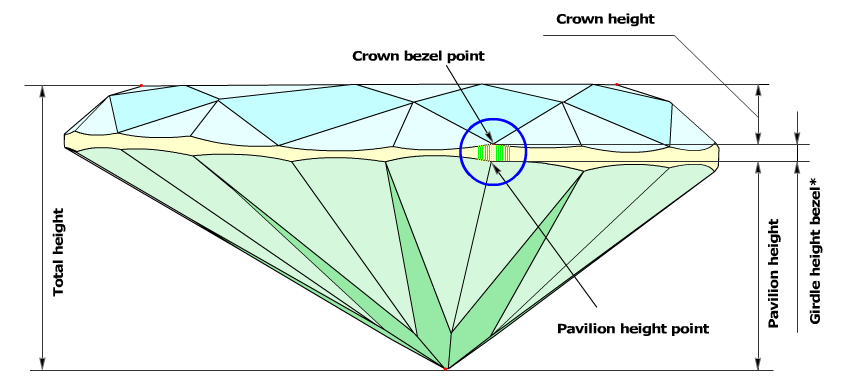
Figure 2a, enlarged view
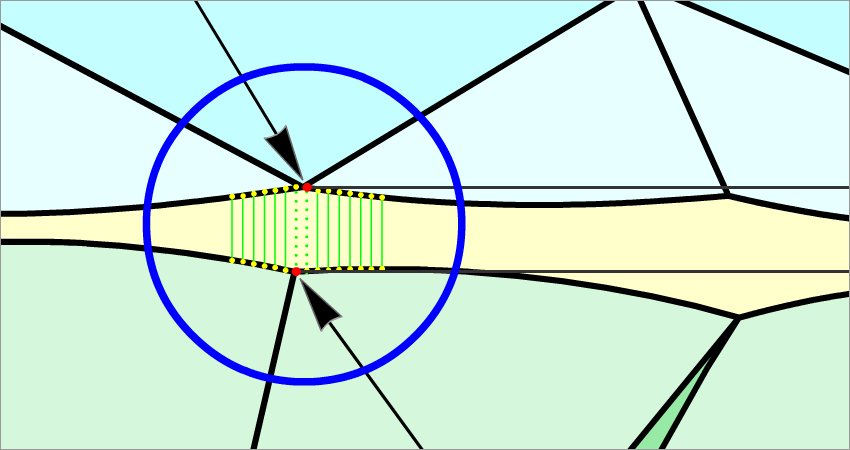
|
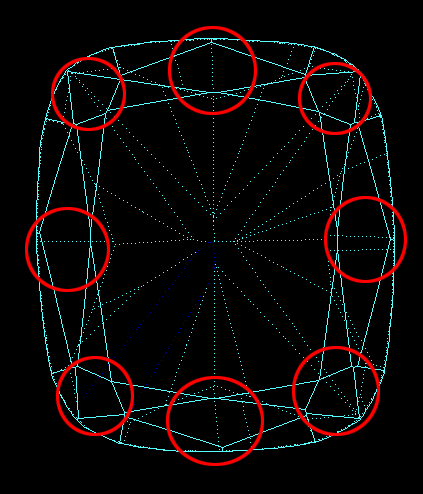
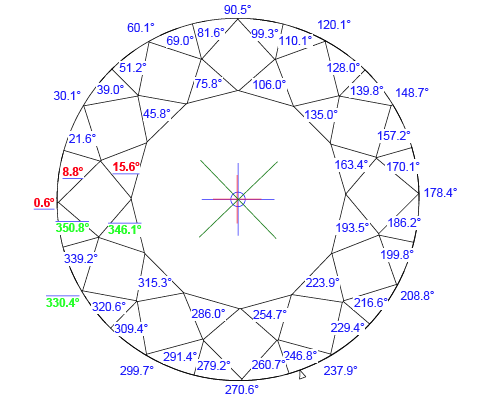
 - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth. - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
 - Crown bezel point and Pavilion height point. - Crown bezel point and Pavilion height point.
|
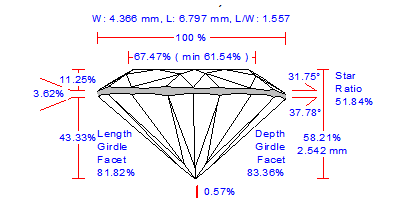
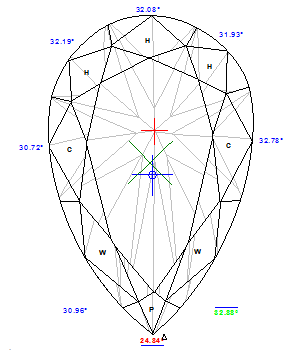
See example of the full report to Pear:
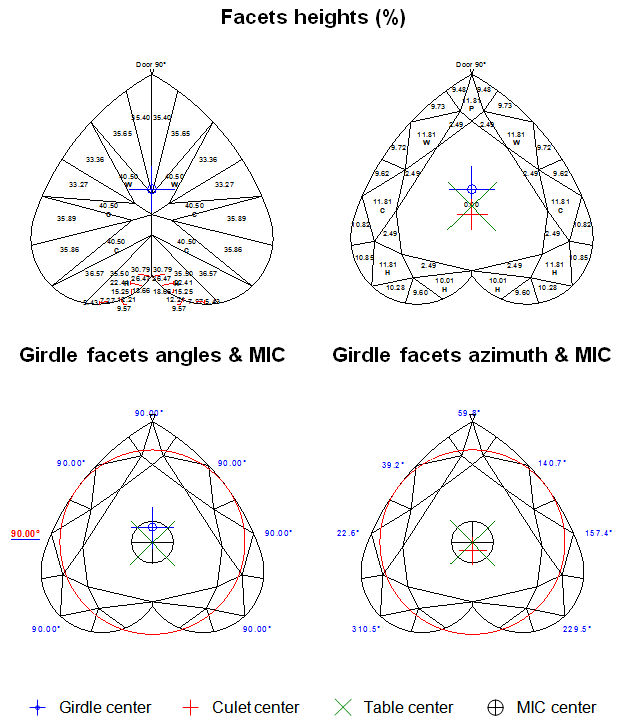
- If the difference between the azimuths exceeds 4 degrees and less then 10 degrees, the value of the Girdle height bezel parameter is the local maximum among several values of the girdle height, which are measured between the Crown bezel point and the Pavilion height point with a step of 0.5 degrees by azimuth (Figure 2b and Figure 2b, enlarged view).
Figure 2b
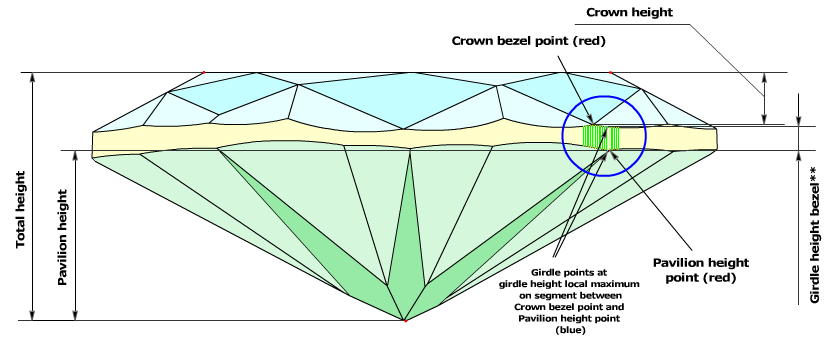
Figure 2b, enlarged view
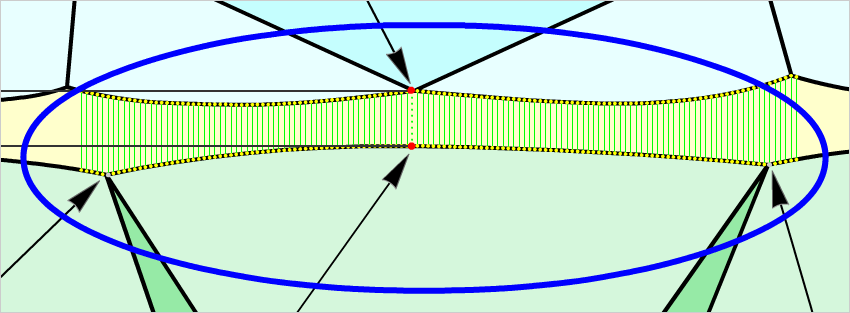
- If differences between azimuths of Crown bezel point and nearest Pavilion bezel points or Pavilion bone points are more then 10 degree, the heights are measured at one azimuth. So, value of the Girdle height bezel is equal to Girdle height with the same azimuth as Crown bezel point. Also Pavilion height point is taken at the point on girdle lower curve with same azimuth as Crown bezel point (Figure 2c and Figure 2c, enlarged view)
Figure 2c
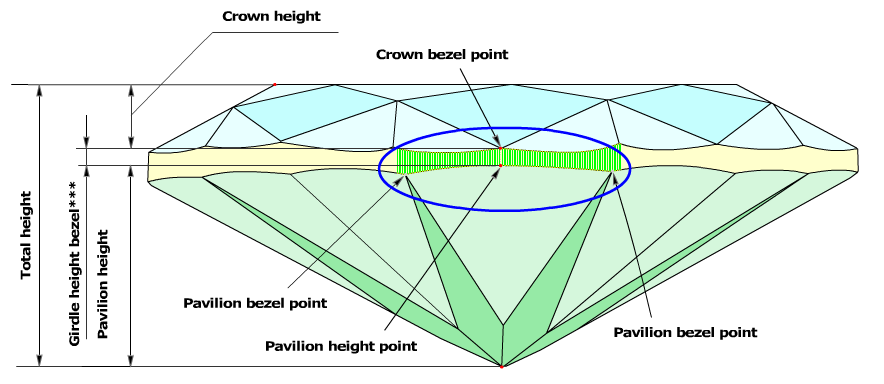
Figure 2c, enlarged view
|
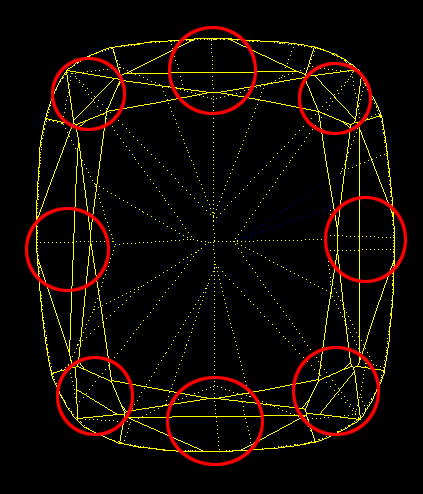
 - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth. - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
|
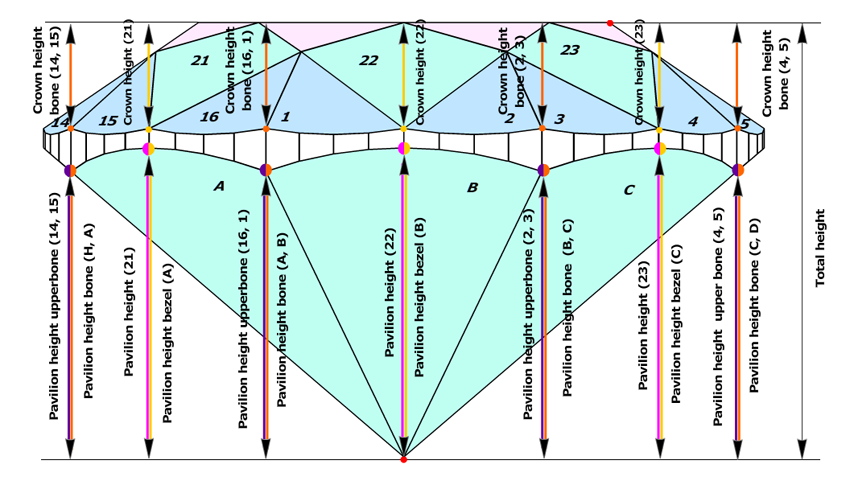
New method of estimating Crown height bone, Pavilion height upperbone and Girdle height bone
The Crown bone points determine the measurement zones of the following parameters: Crown height bone, Pavilion height upperbone, and Girdle height bone.
- The software finds the Crown bone point on the upper girdle curve, by the same method as in old program.
- Then it finds the closest (by azimuth) Pavilion bone point or the Pavilion bezel point on the lower girdle curve, by the same method as in the previous versions. if there are no Pavilion bone point or Pavilion bezel point around Crown bone point, it could be just a point on a lower girdle curve, with the same azimuth as Crown bone point. Let us call it the Pavilion upperbone point.
- The distance, along diamond's axis that perpendicular to table, between maximal distant culet point and this Pavilion upperbone point is called Pavilion height upperbone in the new version of the software (Figure3a, 3b, 3c).
- The difference between azimuths of Crown bone point and Pavilion height point is determined.
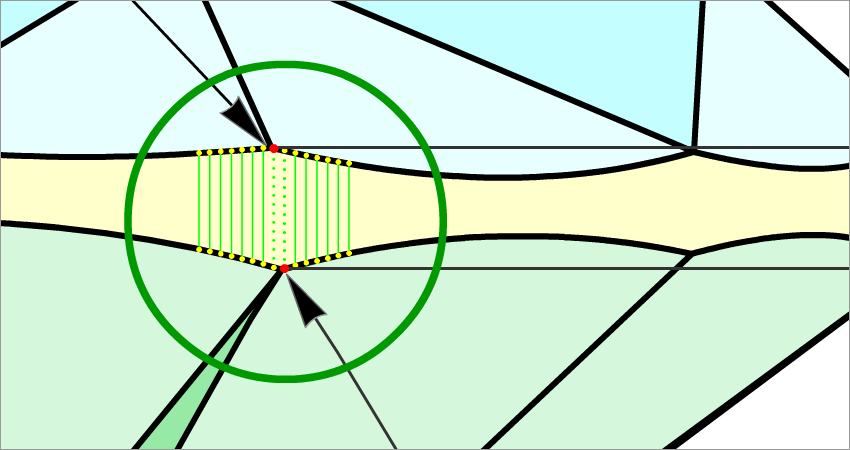
- If the difference between the azimuths of the Crown bone point and the corresponding Pavilion upperbone point is less than 4 degrees, the value of the Girdle height bone parameter is measured as height between the Crown bone point and the opposite Pavilion upperbone point (Figure 3a and Figure 3a, enlarged view).
Figure 3a
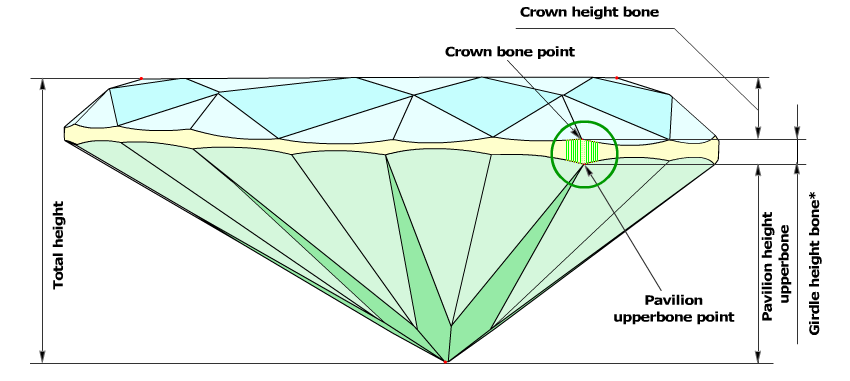
Figure 3a, enlarged view
|
 - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth. - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
 - Crown bone point and Pavilion upperbone point. - Crown bone point and Pavilion upperbone point.
|
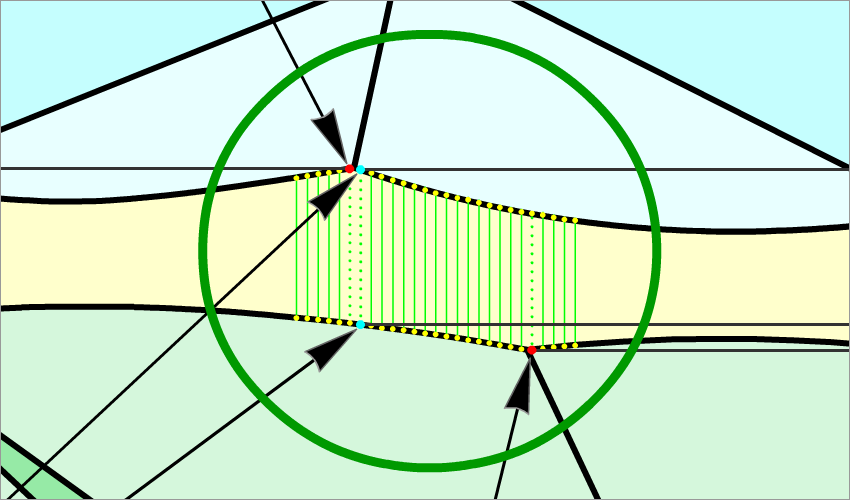
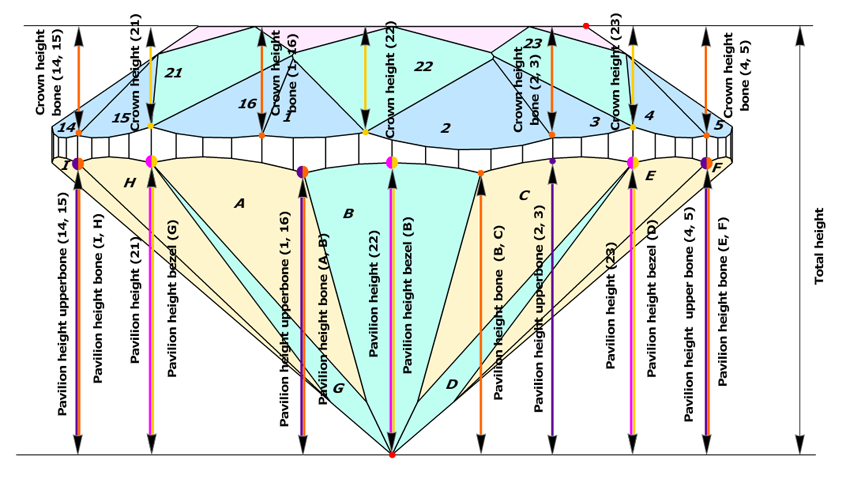
- If the difference between the azimuths exceeds 4 degrees and less then 10 degrees, the value of the Girdle height bone parameter is the local maximum among several values of the girdle height, which are measured between the Crown bone point and the Pavilion upperbone point with a step of 0.5 degrees by azimuth (Figure 3b and Figure 3b, enlarged view).
Figure 3b
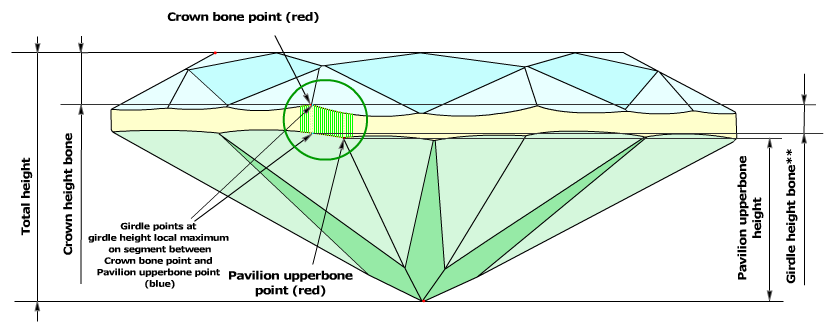
Figure 3b, enlarged view
- If differences between azimuths of Crown bone point and nearest Pavilion bone point or Pavilion bezel point are more then 10 degree, the heights are measured at one azimuth. So, value of the Girdle height bone is equal to Girdle height with the same azimuth as Crown bone point. Also Pavilion upperbone point is taken at the point on girdle lower curve with same azimuth as Crown bone point (Figure 3c and Figure 3c, enlarged view).
Figure 3c
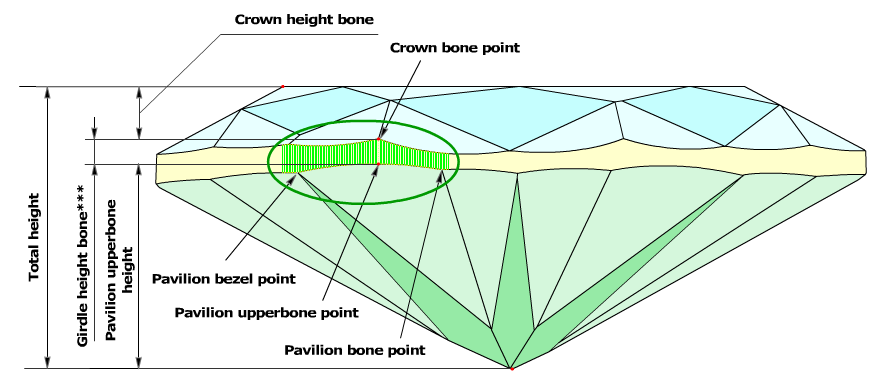
Figure 3c, enlarged view
|
 - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth. - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
|
Consider our several complex examples of measurements of bezel and bone heights.
Example 1. Semi-polished diamond without all upper girdle facets 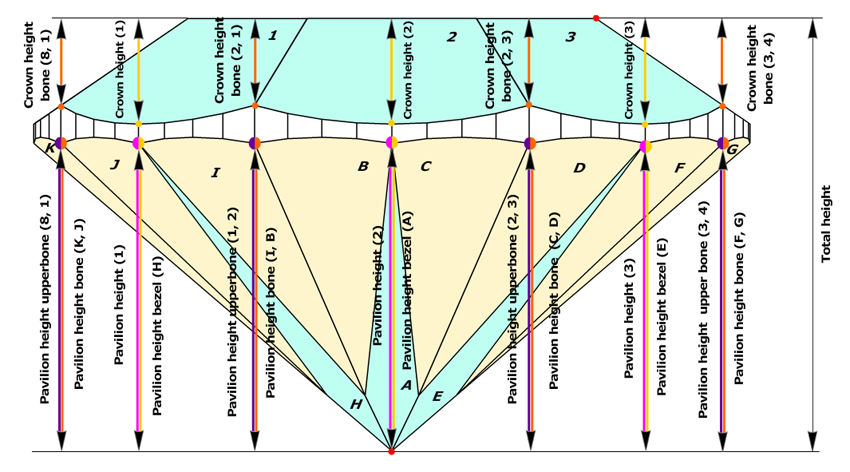
Example 2. Semi-polished diamond without all lower girdle facets
Example 3. Semi-polished diamond without two lower girdle facets and dig-out on crown
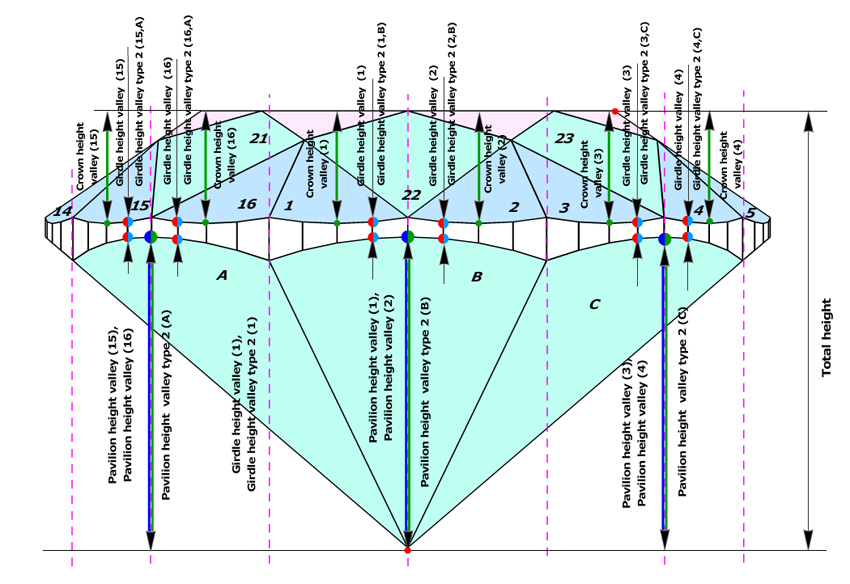
New methods of estimating Valley Heights
We use new way of estimating of heights for valley for Pavilion and Girdle. We developed two new methods: first method bases on measurements of Crown heights valley, second method bases on measurements of the old parameter Pavilion depths at girdle minimum.
The reason for this changes is absence of some measurements for valley heights for semi-polished cuttings with absence of some halves or main facets.
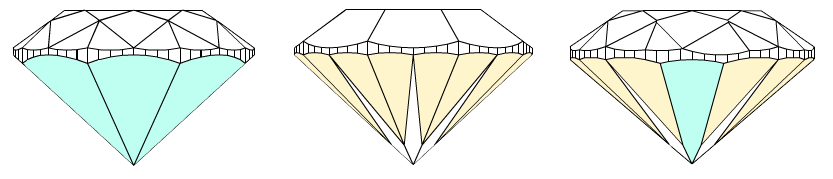
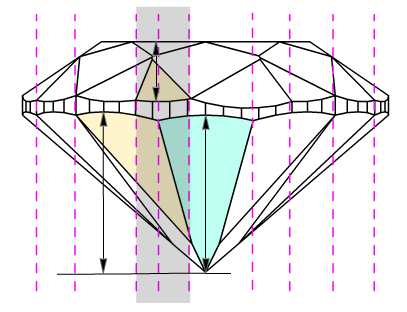
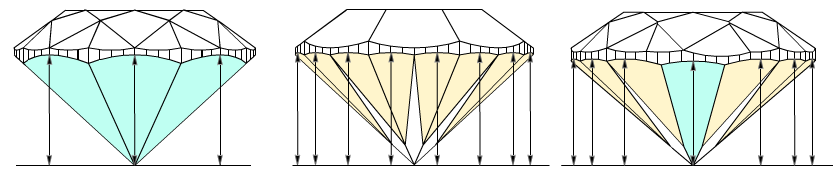
In fact, if upper and lower girdle facets are absent in cutting and model, main facets have longest width in place where it touches girdle and could be considered as zones for valley measurements (marked as yellow on the picture below). But these measurements of valleys heights were absent in previous program versions.
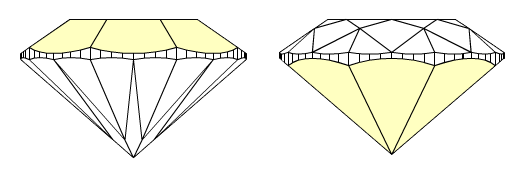
Currently we use term wide-facets for zones of measurements of valley heights. Term wide-facet is a name of a facet on crown or pavilion that could be any type: main facets, upper, lower facets and any other, if it has a longest width in place where it touches girdle (marked as yellow on the picture below). Usually, upper and lower girdle facets are wide-facets. Main facets could be wide-facets in semi-polished diamonds, while upper and lower girdle facets are not made yet.
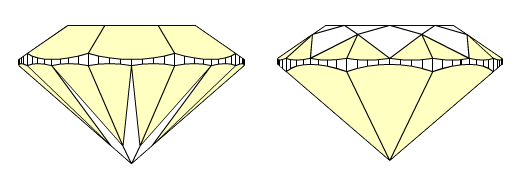
First method, type 1, is based on parameter Crown height valley. Crown height valley parameter can be measured on any wide-facet on crown. Crown height valley parameter defines measurement for Pavilion height valley and Girdle height valley parameters. As a result we have the same quantities of Crown height valleys, Pavilion height valleys and Girdle heights valleys, in spite of having different quantities of crown and pavilion facets.
Second method, type 2, is based on Pavilion wide-facet maximum heights. The new parameter Pavilion height valley type 2 derives from the similar old parameter Pavilion depth at girdle minimum. However, Pavilion depth at girdle minimum measured maximum height for lower girdle facets only, whereas new parameter Pavilion height valley type 2 measures maximum height for any wide-facet on pavilion (lower girdle facets, wide-facet main facets), as well. Pavilion height valley type 2 defines Girdle height valley type 2.
Description of first method, type 1
First method uses Crown height valley for definition Pavilion height valley and Girdle height valley parameters. It provides with the same quantities of Crown, Pavilion and Girdle height valley measurements.
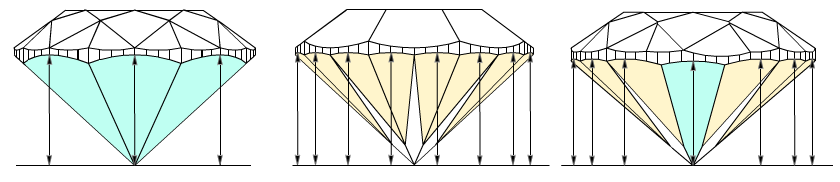
1) First of all, Crown heights valley are measured as maximum facet heights on crown wide-facets:
- The wide-facets on crown are determined. On the picture, wide-facets, like upper girdle facets, marked as orange; wide-facets, like mains facets, marked as green.
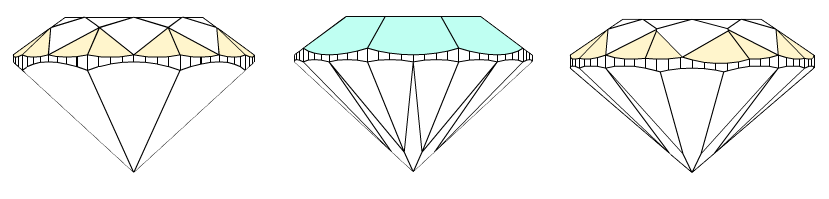
- Maximum height is measured for each crown wide-facet. On the picture marked by arrows. That are Crown height valleys.
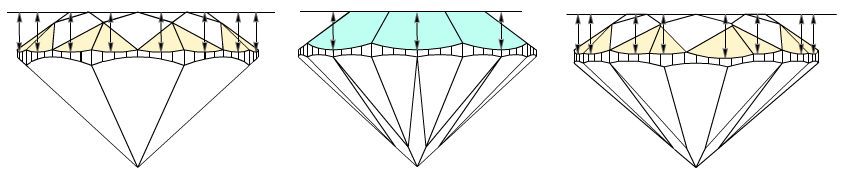
2) Next, the program finds zones for future Pavilion height valley and Girdle height valley measurements:
3) Estimating Girdle height valleys and Pavilion height valley
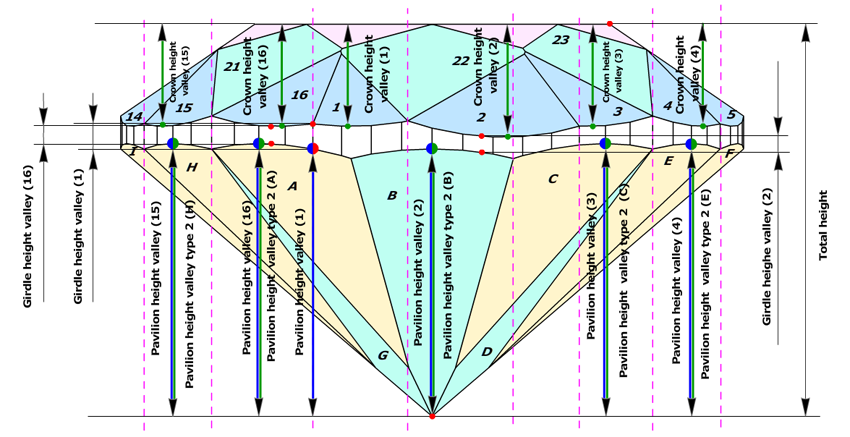
Description of second method, type 2
Second method uses Pavilion wide-facet maximum heights for definition Pavilion height valley type 2 and Girdle height valley type 2 parameters.
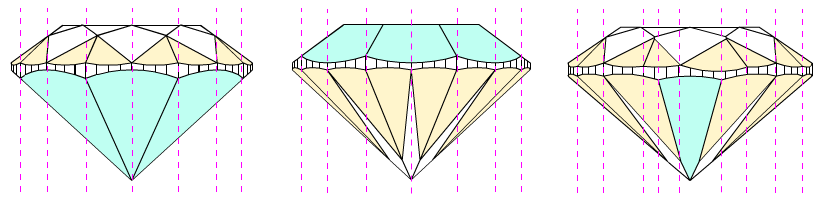
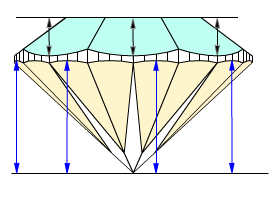
The measurement for parameter Pavilion height valley type 2 (black arrows on the picture) are the same as Pavilion wide-facet maximum heights that described above (see description for Fist method, type 1, section 2).
Moreover, Pavilion height valley type 2 is similar to old parameter Pavilion depth at girdle minimum. However, Pavilion depth at girdle minimum measures heights for lower girdle facets only, new parameter Pavilion height valley type 2 measures maximum heights for all wide-facets on pavilion.
Girdle height valley type 2 parameter defines the same way as Girdle height valley type 1 (see description for Fist method, type 1, section 3)
Comparison two systems of measurements, type 1 and type2
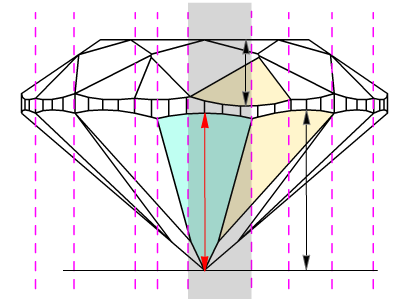
The difference between Pavilion heights valley and Pavilion height valley type 2 are shown on the picture below. Left picture illustrates measurements of Pavilion heights valley, by first method (blue arrows), and right picture illustrates measurements of Pavilion heights valley type 2, by second method (green arrows). Crown height valley are shown by black arrows. We introduced parameter Pavilion height valley type 2 not to lose measurements are shown on the right picture.
 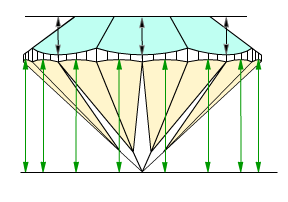
Consider our several complex examples of measurements of valley heights for more details.
Example 1. Semi-polished diamond without all upper girdle facets 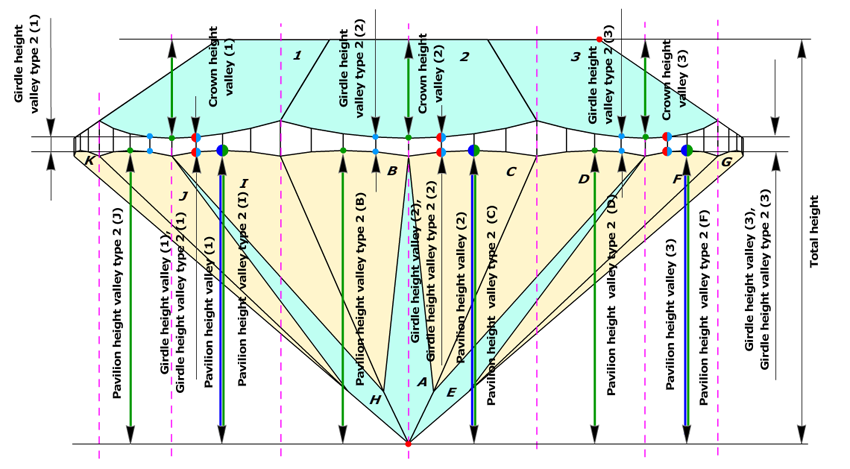
Example 2. Semi-polished diamond without all lower girdle facets
Example 3. Semi-polished diamond without two lower girdle facets and dig-out on crown
Additional notices
1) The method of accounting of naturals and extra facets remains unchanged and is not affected by the new method for measuring the crown, pavilion, and girdle heights.
2) Pavilion depth is renamed to the Pavilion height bezel parameter.
Total depth is renamed to the Total height parameter.
The old parameters are still available and can be accessed by using the new bookmarks listed below:
| Name of old parameter |
Name of new parameter |
Old bookmark |
New bookmark |
| Pavilion Depth |
Pavilion height bezel |
PAVILION_DEPTH_ |
PAVILION_HEIGHT_BEZEL_ |
| Total depth |
Total height |
TOTAL_DEPTH_ |
TOTAL_HEIGHT_ |
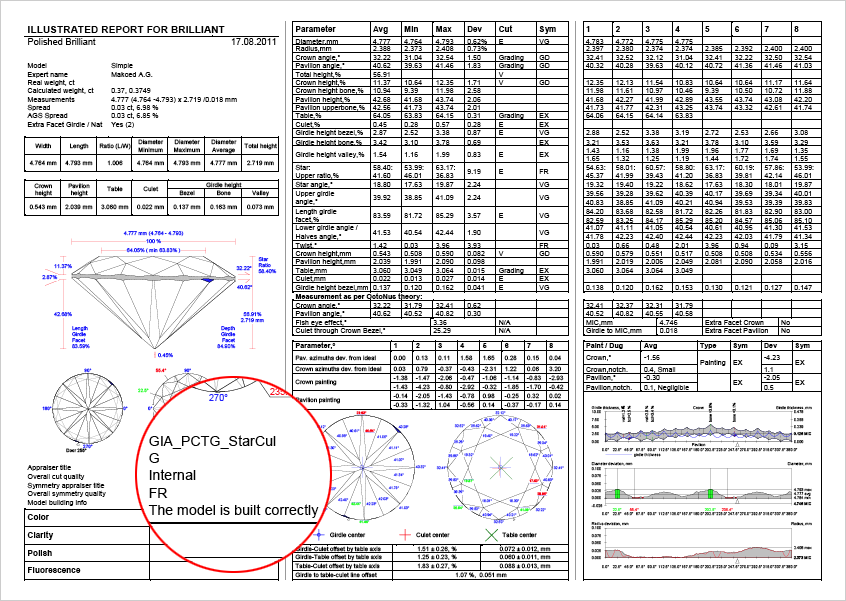
New version of full report contains united together full reports for polished and semi-polished diamonds |
|
We created new version of Full report that united together full report for polished and semi-polished diamonds. It has the same name like old Full reports for polished diamond, Full report for brilliant or Full report for rounded fancies.
See some examples of new reports:
Since new version of Full report contains all data from old report for semi-polished, the old Full report templates for semi-polished were removed from template set.
Reports for cuttings with 10, 12 or more main facets, like Solasphera |
|
Reports for cuttings that contain 10, 12 or more main facets, like Solasphera, are improved. For example, all values of 12 main facets, as well as values of all upper and lower facets, are output into the pictures of angles, azimuths and heights in the new version, whereas values for 8 main facets only were output in the previous versions. The statistic values of parameters take into account all 12 main facets, not only facets that restricted by quantity 8.
See example of new report:
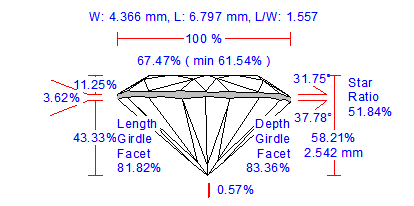
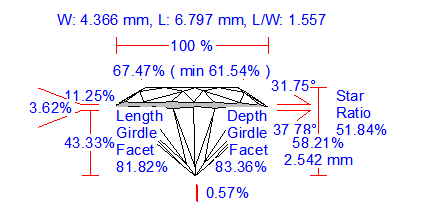
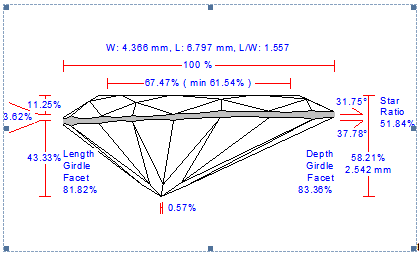
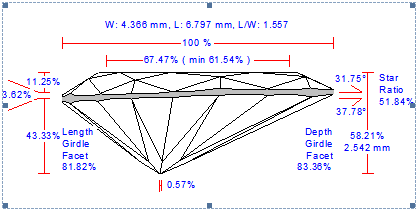
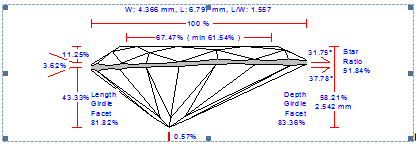
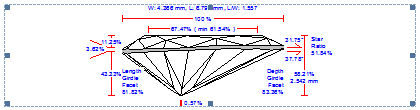
New Options for Picture Profile View Report |
|
General description
We improved a picture Profile View Report. There are four new options customized via INI file:
- Rotation about the vertical axis
- Font size scaling
- Aspect ratio customization
- Line thickness adjustment
To include a picture Profile View Report into any report add the follow section into INI file:
[Picture3]
PictureID=PROFILE_VIEW_REPORT
Bookmark=SUMMARY_REPORT_WIDTH
FontSize=120
NormalLineThickness=30
BoldLineThickness=40
AutoAspectRatio=1
Z=0
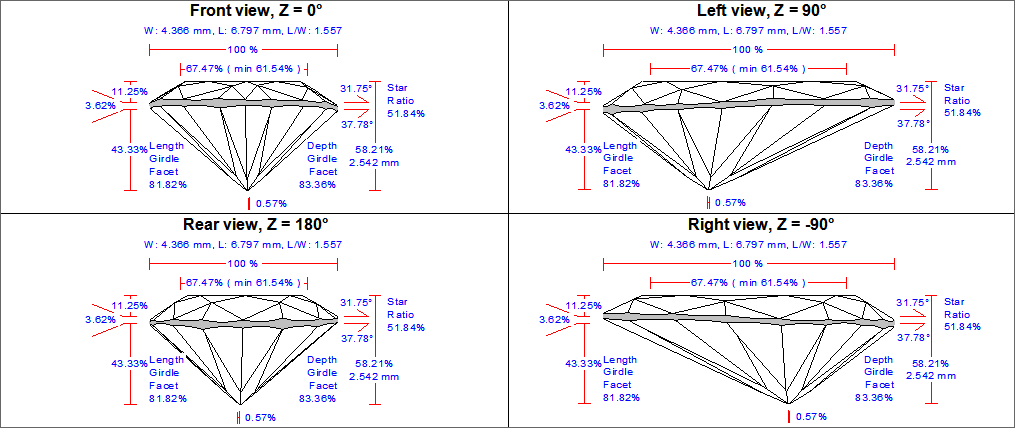
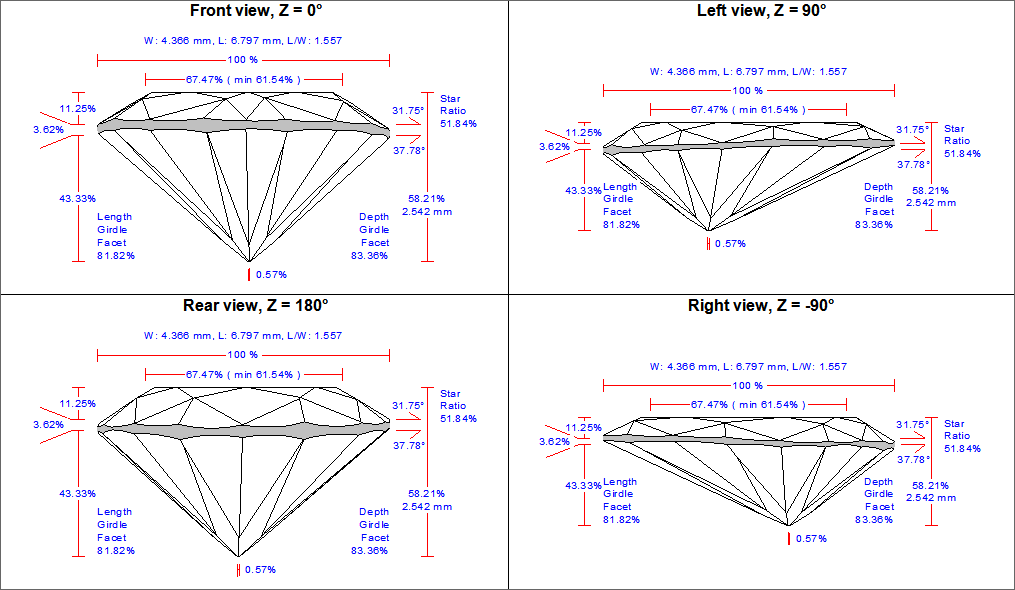
To add more picture add more sections [Picture..] into INI file. See the example below for adding three more picture with rotation about the vertical axis 90, 180 and -90 degrees.
[Picture4]
PictureID=PROFILE_VIEW_REPORT
Bookmark=SUMMARY_REPORT_LENGHT
FontSize=120
NormalLineThickness=30
BoldLineThickness=40
AutoAspectRatio=1
Z=90
[Picture5]
PictureID=PROFILE_VIEW_REPORT
Bookmark=SUMMARY_REPORT_WIDTH_REAR
FontSize=120
NormalLineThickness=30
BoldLineThickness=40
AutoAspectRatio=1
Z=180
[Picture6]
PictureID=PROFILE_VIEW_REPORT
Bookmark=SUMMARY_REPORT_LENGHT_RIGHT
FontSize=120
NormalLineThickness=30
BoldLineThickness=40
AutoAspectRatio=1
Z=-90
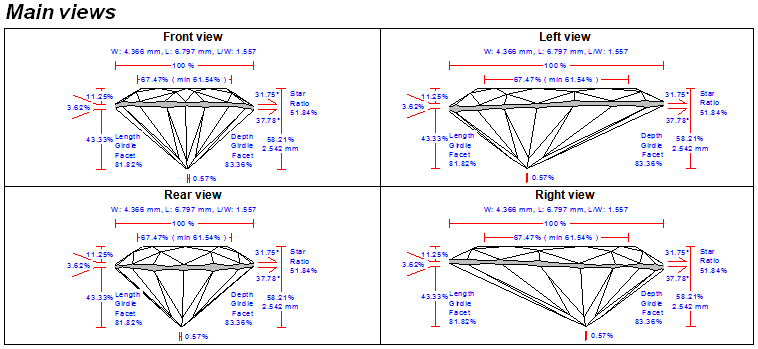
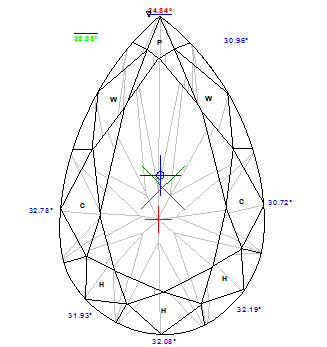
See example of the full report to Pear:
|


 - Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
- Two range of points that located on girdle lower curve and girdle upper curve. Every range has 720 points with step 0.5 degree by azimuth.
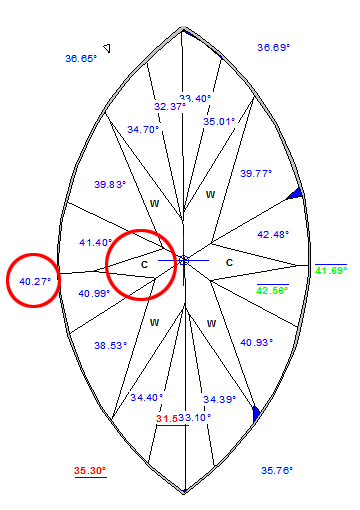
 - Crown bezel point and Pavilion bezel point.
- Crown bezel point and Pavilion bezel point. - Girdle points at local maximum of Girdle heights.
- Girdle points at local maximum of Girdle heights.