|
From the materials of Pricescope
Diamond Journal
"Lasers used in planning the cutting of diamonds"
by Garry Holloway
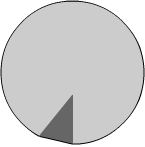
All scanners build 3D virtual models by photographing the shadow
profile of a rotating gem in front of a light source. But this method
misses concavities (see the example in first image). Using the 'triangulation
principle' a low power visible line (e.g. from a 'lecture pointer'
type laser beam) is directed onto the rough gemstone from an oblique
angle of about 30° to the camera. From the cameras perspective a
convex object, like a sphere, shows a line curving away from the
center, but the light shines into any concavities or holes, and
the camera sees an inward curving line. Software calculates the
depth of the concavity and adjusts the 3D model.
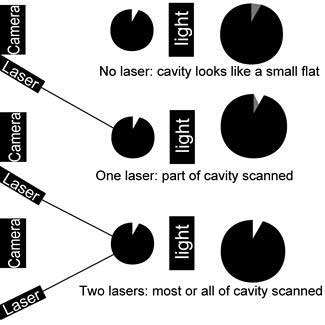
OctoNus developed a dual laser cavity mapping system that gets
to the bottom of more holes than the single red laser light system
as shown in the example below.
Two Helium Rough camera views (the first in shadow profile mode) of irregular shaped rough diamonds showing two laser lines (in black and white). Concave distortion in the vertical beams from the two laser beams show the rough has cavities. These cavities are not able to be detected in the shadow edge silhouette.

Dual Laser mapping
What is Dual Laser cavity mapping? How does
it work? Why Dual Laser mapping is better then Single Laser mapping?
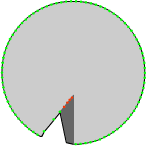
There are two samples with models obtained by different types of
scanning in the table below. The detailed descriptions, diagrams
and movies are available.
Examples of models obtained by different types
of scanning
|
|
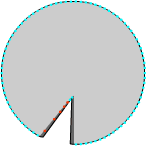
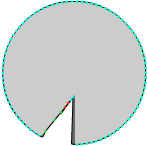
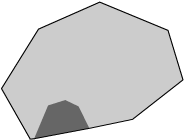
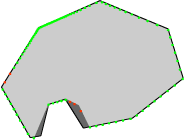
Shadow model |
Laser mapping model by one laser
Laser beam from left |
Laser mapping model by one laser
Laser beam from right |
Dual Laser mapping model
The cumulative result |
| Movies: Sample 1 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Movies: Sample 2 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Coins
There are Dual Laser mapping models of coins obtained on Helium
Rough 1:4D scanner. You can download and explore .oxg demo files
with Oxygen Viewer Free Version
and Oxygen Inclusion.
50 Cents, New Zealand
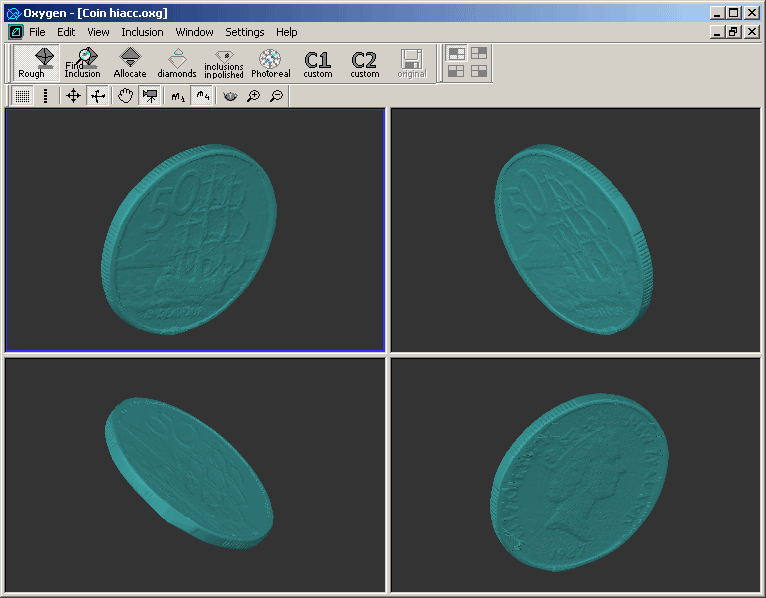
Download coin_hiacc.oxg
5 Rand, Republic of South Africa
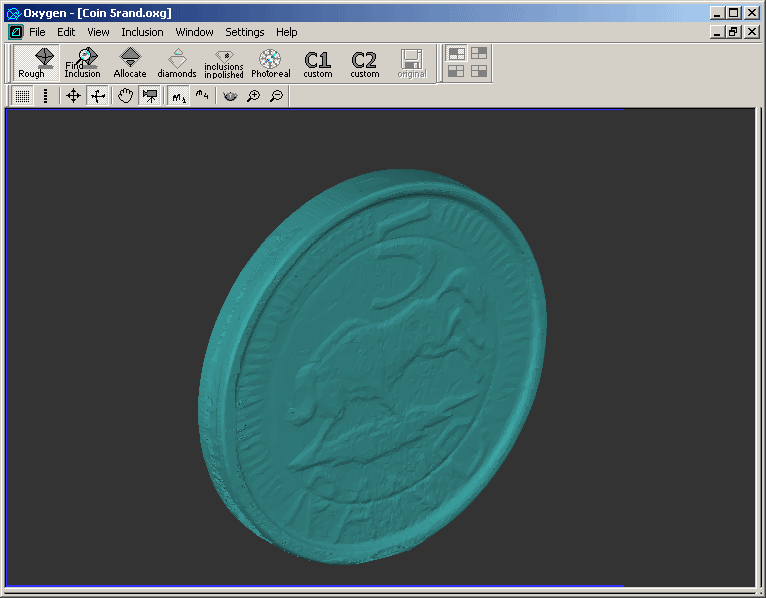
Download coin_5rand.oxg
|